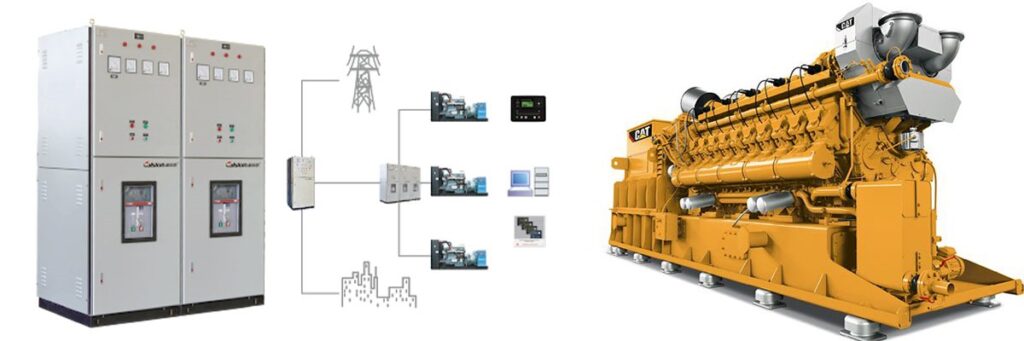
A Power Distribution Board (PDB), also known as a Power Distribution Panel or Electrical Distribution Board, is a crucial component in an electrical distribution system. It manages and distributes electrical power to various circuits or devices within a building or facility. Here’s an overview of its key functions and components

ELECTRIC LOW VOLTAGE PANEL
MAIN DISTRIBUTION BOX APFC PANEL AUTO CHNAGE OVER PANEL MCC PANEL VFD & SOFT STARTER PANEL SYNCHRONIZING PANELFollow Us:
Functions of a Power Distribution Board:
Safety: By centralizing the distribution and protection of electrical power, the PDB enhances safety by reducing the risk of electrical hazards and ensuring compliance with electrical codes and standards.
Power Distribution: The PDB distributes electrical power from the main supply to various branch circuits throughout the building or facility. It ensures that power is evenly and safely distributed to different areas and equipment.
Protection: It houses protective devices such as circuit breakers or fuses that safeguard the electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. These devices automatically disconnect power if a fault is detected, preventing damage to the wiring and connected equipment.
Control: The PDB may include switches or controls that allow operators to manage the power supply to different circuits or areas. This can facilitate maintenance and troubleshooting by isolating specific circuits without affecting the entire system.
Monitoring: It can include meters and indicators that provide information on electrical parameters such as voltage, current, and power consumption. This helps in monitoring the system’s performance and detecting any issues.
Key Features
- Functionality:
- The PDB receives electricity from a primary source, such as a transformer or generator, and distributes it to multiple circuits.
- It acts as a central hub for managing power distribution within residential, commercial, or industrial settings.
- Components:
- Circuit Breakers: Protect circuits from overloads and short circuits by interrupting the flow of electricity when necessary.
- Busbars: Conduct electricity and distribute it to various outgoing circuits.
- Fuses: Provide an additional layer of protection for specific circuits.
- Control and Monitoring Systems: Allow for the tracking of electrical usage and performance, often integrating with building management systems.
- Types:
- Single-phase and Three-phase: Depending on the electrical requirements of the facility, PDBs can be designed for single-phase or three-phase systems.
- Modular Design: Some PDBs are modular, allowing for easy expansion or reconfiguration as power needs change.
Components
-
Main Breaker or Fuse
-
Circuit Breakers or Fuses
-
Busbars
-
Neutral and Ground Bars
-
Meters and Indicators
-
Terminal Blocks
-
Enclosure
Applications
-
Residential Buildings
-
Industrial Facilities
-
Commercial Buildings
